Explain Different Classes of Ip Address and Their Addressing Scope
Communication can be one to one one to many and one to all. Since Class A rules the first byte we left with 3 bytes for the Hosts.
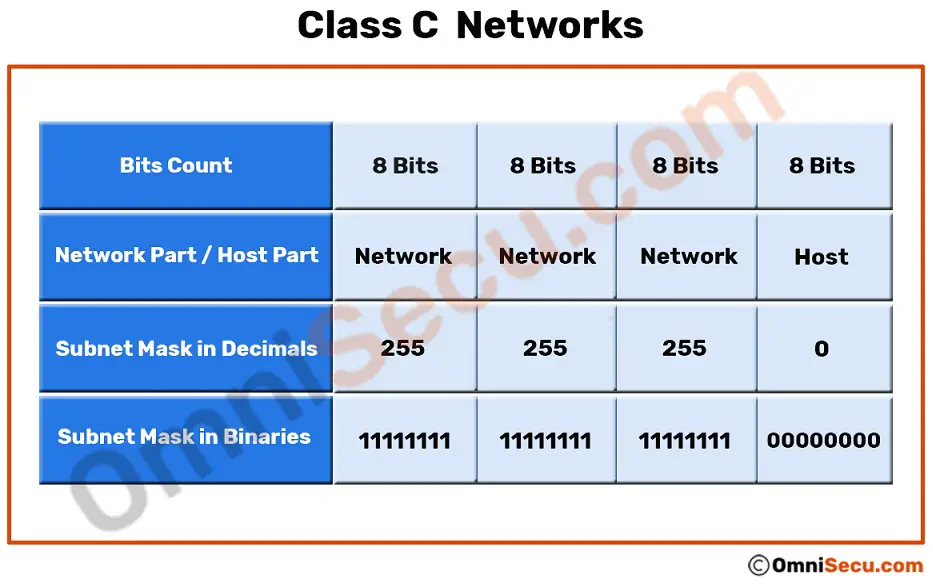
Class C Networks And Class C Ip Addresses
In multicasting data is not destined for a particular host that is why there is no need to extract host address from the IP address and Class D does not have any subnet mask.
. The second half of the address last 64 bits is always used for Interface ID. The MAC address of a system is composed of 48-bits and represented in Hexadecimal. There are 16384 possible Class B networks.
This tutorial explains DHCP and its types in detail. Type the range of IP addresses that will be available to clients on a particular subnet as shown in Figure 32. The first three bits of the most significant octet of an IP address were defined as the class of the address.
Only classes A B and C are available for commercial use. Type a range or single IP address that you want excluded see Figure. Learn what the DHCP is and what are the advantages and disadvantages of having a DHCP server in the network.
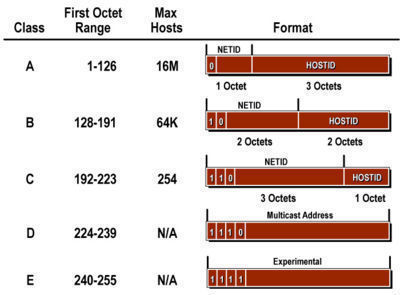
Figure 30-3 An IP address consists of 32 bits grouped into four octets. Class D is reserved for Multicasting. So the full IP addressing range goes from 0000 to 255255255255.
A BC D and E. MAC addresses are considered to be uniquely assigned worldwide. Depending on the class derived the network identification was based on octet boundary segments of.
Three classes A B and C were defined for universal unicast addressing. The same goes for class A addresses. Interface ID takes advantage of this uniqueness of MAC addresses.
Each number can range from 0 to 255. An IPv6 unicast address is globally routable on the public internet. The left-most high-order bits indicate the network class.
Types of IP addresses have been classified based on communication with each other in a computer network. The IP protocol defines five different address classes. In the following we will describe each type of IP address in detail with an example.
Generally public IP addresses can be of two types. IPv6 has three different types of Unicast Address scheme. This IP Class is reserved for experimental purposes only for RD or Study.
Other different type of unicast addressing is Global Link local Site local. Hosts 2 24 16777216 2 16777214 Hosts or Usable IP address Per Network. Each device in an IP network requires a valid IP configuration.
Apart from IP addresses its worth. The IP address with a first octet from 128 to 191 is part of this class. When you get your IP address from your ISP you either get a Static or a Dynamic IP address.
In class C the first 24 bits are. This time we have a lot more bits to borrow and this is probably the most flexible one in terms of subnetting. Class E is experimental so you can just forget about those too.
An IP address is always a set of four numbers like that. In dotted decimal notation that makes 128000 to 19125500 as Class B networks. In class A the first bits are reserved for the network addressThe remaining 24 bits are available for the host address.
We all have the experience to work with the unicast. If the network size is small an administrator can manually provide an IP configuration to each device. 21342132 Class B In a Class B network the first 16 bits are the network part of the address.
A DHCP scope is a range of IP addresses that are available for the DHCP servers to lease out to DHCP-enabled clients on a given subnet. 100008 10000 10255255255 172160012 1721600 17231255255 1921680016 19216800 192168255255 Anybody can use these private ranges for anything they like. Class C is used for small to middle size networks.
By even casual observation youll likely have noticed that there are several IP address ranges that are special including. All Class B networks have their first bit set to 1 and the second bit set to 0. Class A networks accounts for half of the total available IP addresses.
Interestingly users can create as many scopes as required on a DHCP server. Class D has IP address range from 224000 to 239255255255. This is the most common type of address.
It is used for medium size networks. Its primary function is to decide which IP addresses the servers get to offer the clients. A B C D and E.
In class B the first 16 bits are reserved for the network address while the last 16 bits are available for the host address. IP Address Classes IP addressing supports five different address classes. The first three classes vary the portion of the address devoted to the network ID and the host ID.
Static and Dynamic IP addresses. Class B networks have a first bit value of 1 and a second bit value of 0 in the first octet. Defining the range of IP addresses within a scope.
Each IP class consists of a contiguous subset of the overall IPv4 address range. Lets look at these IPv6 address types in detail below. Class D is for multicast addresses which is something else entirely.
This can also refered to as one to-one ipv6 address. The IPv4 IP address space can be subdivided into five address classes called Class A B C D and E. Example for a Class A IP address.
The reason each number can only reach up to 255 is that each of the numbers is really an eight digit binary number sometimes called an octet. What Are The Classes Of Ipv4 How To Identify Ip Class From A Given Ip Address Ip Address Classes Tech Faq Pin On Estudiar Class C Networks And Class C Ip Addresses. The length of network addresses and host addresses in IP addresses are different in all IP classes.
One such class is reserved only for multicast addresses which is a type of data transmission where more than one computer is addressed information at once. Packets addressed to a unicast address is destined for a single interface. The subnet mask is automatically defined but can be changed if your network is subnetted.
126 Networks x 16777214 2113928964 2 Billion something Usable IP addresses Based on 128 256 50 Class A IP addresses represent almost 50 of the Original IP Space Total. Static IPs are static as their name suggests ie they do not change. That is probably why one of the most popular private IP addresses or network addresses is the network 10 the class A private address.
However private IPs can also have static or dynamic IP addresses.
How Is An Ip Address Classified Quora

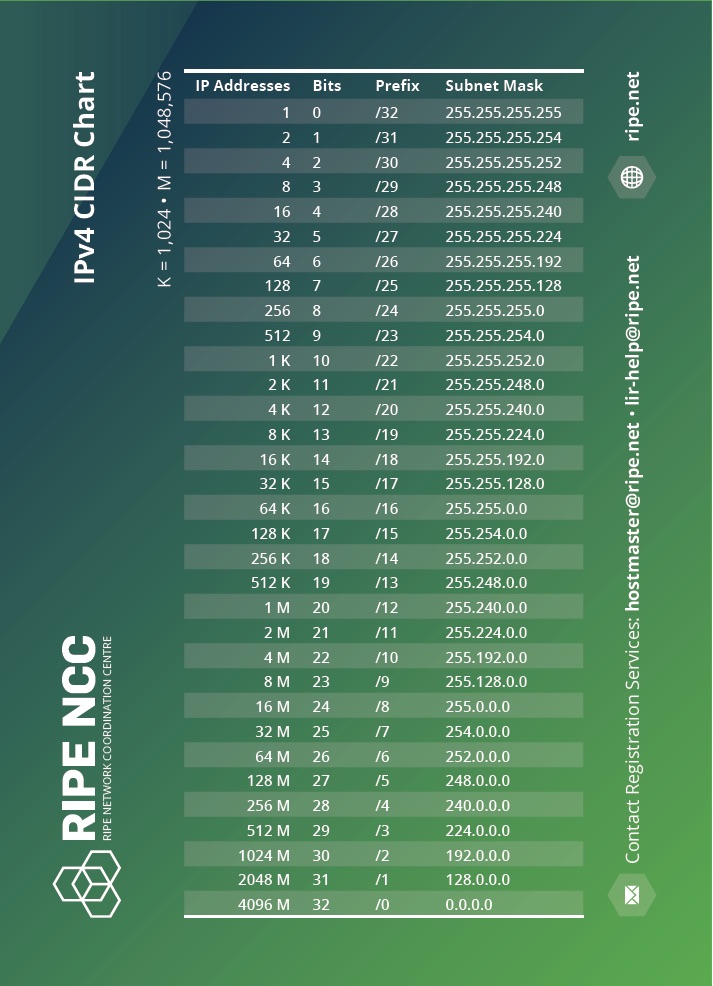
Understanding Ip Addressing And Cidr Charts Ripe Network Coordination Centre
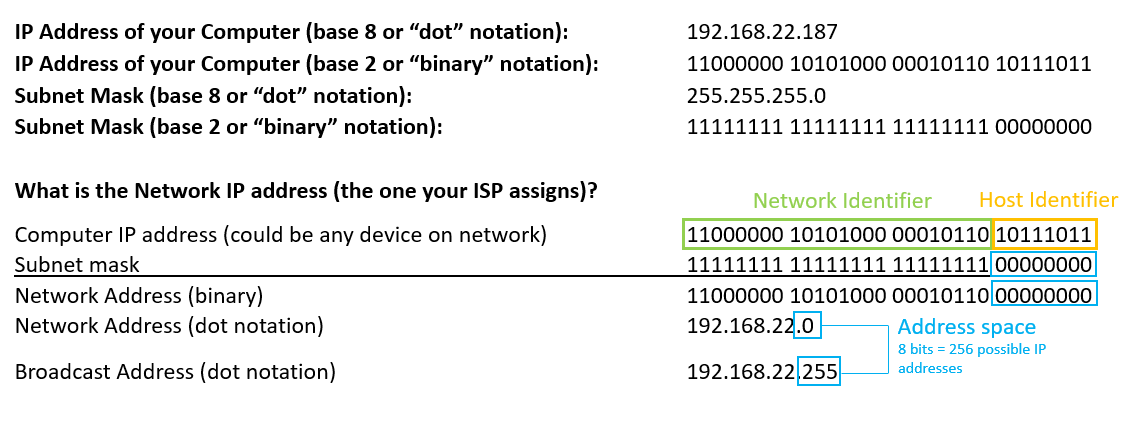
Understanding Ip Addresses And Subnet Masks By Zach Gollwitzer Medium
Ip Addresses Subnet Masks And Ip Networks Homenet Howto
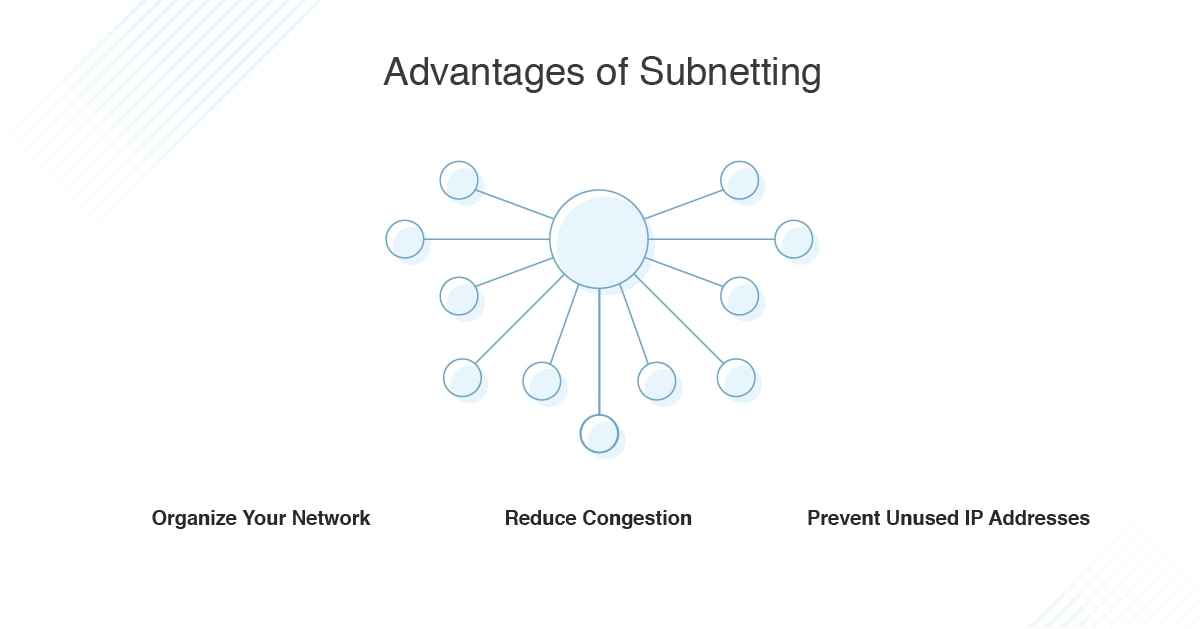
Subnet And Subnetting Tutorial Guide Dnsstuff

What Are The Classes Of Ipv4 How To Identify Ip Class From A Given Ip Address

The Abcs Of Ip Addresses Pcmag
Ip Addresses Subnet Masks And Ip Networks Homenet Howto
![]()
8 Best Ip Address Trackers Dnsstuff
Ip Addresses Subnet Masks And Ip Networks Homenet Howto

What Are The Classes Of Ipv4 How To Identify Ip Class From A Given Ip Address
/Public-vs-local-IP-addresses.png?width=1320&name=Public-vs-local-IP-addresses.png)
Public Or Private Ip Address What S The Difference Avg

Ipv4 Address An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Comments
Post a Comment